

- #Vagrant commands how to#
- #Vagrant commands update#
- #Vagrant commands password#
- #Vagrant commands download#
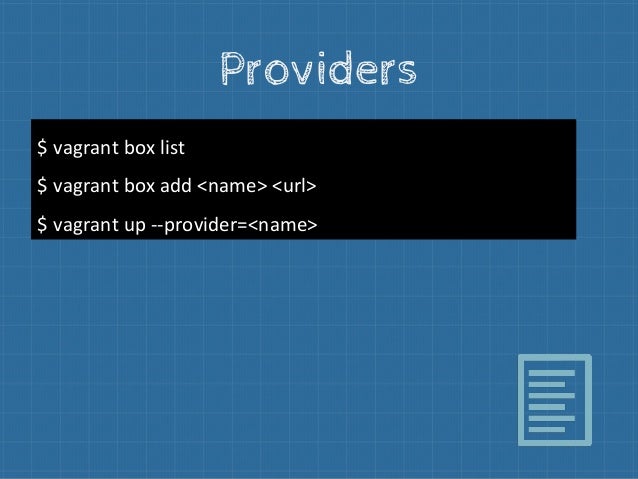
Bring up all Detection Lab hosts using VMware: vagrant up –provider=vmware_desktop.Bring up all Detection Lab hosts using Virtualbox: vagrant up –provider=virtualbox.Basic Vagrant UsageĪll commands must be run from the “DetectionLab/Vagrant” folder If you happen to have both Virtualbox and VMware Workstation/Fusion installed, it may be helpful to set the VAGRANT_DEFAULT_PROVIDER environment variable to either vmware_desktop or virtualbox.
#Vagrant commands how to#
In the next article, we will take a look at how to use shell provisioners and automate your vagrant boxes deployment.When running Vagrant commands, you must be in a directory containing a Vagrantfile or you will receive the following error: A Vagrant environment or target machine is required to run this command. To remove the vagrant box run: $ vagrant box remove ubuntu/focal64 To destroy a vagrant box run the vagrant destroy command, which will delete all the files including disk images but will not delete the downloaded box from the vagrant site.
#Vagrant commands update#
$ vagrant box update -box ubuntu/focal64 -provider Virtualbox
You have to destroy your current box and spin up the new downloaded updated box. An important point to note here is updates will not be applied to the current box you are running.
#Vagrant commands download#
To download the updates, run the following command. $ vagrant box outdated -global => check for an outdated version of all boxes in your machine You can check if your box is up to date by running the following command. The vagrant reloads command brings down the VM gracefully and brings up the VM with new configurations if any. If you suddenly decide to change any parameter in your vagrant configuration file then you have to reload the machine. $ vagrant resume ⇒ Resume the suspended VM $ vagrant suspend ⇒ Put the Machine into a suspended state $ vagrant halt ⇒ Gracefully shutdown the VM To stop a running VM run the following command. Now instead of running vagrant ssh, you can run the traditional ssh connection command. $ sudo sed -i "/^*PasswordAuthentication]no/c\PasswordAuthentication yes" /etc/ssh/sshd_config
#Vagrant commands password#
This will set password authentication to true. Now if you wish to enable password-based authentication for your virtual machine, then run the following command in your VM. Once your vagrant virtual machine is up you can go to your virtualbox GUI manager and verify if all the configurations are as per the defined value. The hostname is also updated and the IP address specified in the vagrant file is also created. You can get this information from the global-status command. If you have multiple machines then you can connect to the specific machine using their ID or Name. Now to connect with the virtual machine simply run the “ vagrant ssh” command. Now if I run the vagrant up command it will configure my virtual machine according to the custom parameter I declared in the vagrant file. Vmbox.vm.provider “virtualbox” do |vmvbox| Virtualbox has five different networking modes and you can choose whichever suits your use case. Setting up my virtual network to bridged adapter mode and assigning an IP address. You have to set “disabled: true/false” to turn on or off the shared folders. Turning off the default synced folder and adding my customized folder. Vmbox.vm.synced_folder “/home/karthick/shelltips”, “/vagrant/shelltips”, disabled: false “Default” will be assigned if you are not defining the name. Let me explain all these parameter’s usage.
Vmbox.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vmvbox| Vmbox.vm.synced_folder "/home/karthick/shelltips", "/vagrant/shelltips", disabled: false Vmbox.vm.synced_folder ".", "/vagrant/", disabled: true # -*- mode: ruby -*-Ĭonfig.vm.allow_hosts_modification = true Now let’s modify and add the following parameters to our vagrant file. $ mkdir ~/vagrant_testingįrom the below image you can see I have created a minimal configuration file using the -m flag with vagrant init command. Let me create a new project folder “ vagrant_testing” and under this run, the vagrant init command to set up a new project. In this article, we will focus on customizing the vagrant file according to our requirements and see important commands to work with the vagrant. In the previous article, we have seen how to spin up a virtual machine using vagrant.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
